Users, Audience, & Identification
The Audience of your product is all users who interact with it. The GetintheLoop Platform uses a very flexible style of identifying and tracking users to support any number of use cases and login systems.
There are 3 states a user can be in:
- Anonymous - ie. anonymous
- Identified - Associated with a unique user id, but not verified
- Verified - Associated with a unique user id, and verified via a signed token
While identifying users is optional, it is required for features like Bookmarking and Limited Offers that require a persistent record of who the user is across app sessions.
Typically, you would identify each user on sign in or auth refresh, alongside your existing authentication logic, and would log them out of the SDK when they sign out of your app.
Verification
In order to verify your product's users, a unique token for each user must be generated and provided with the identify calls. Verification ensures that users cannot impersonate each other, and is required for certain features like Offer Bookmarking.
A typical process for this would look like this:
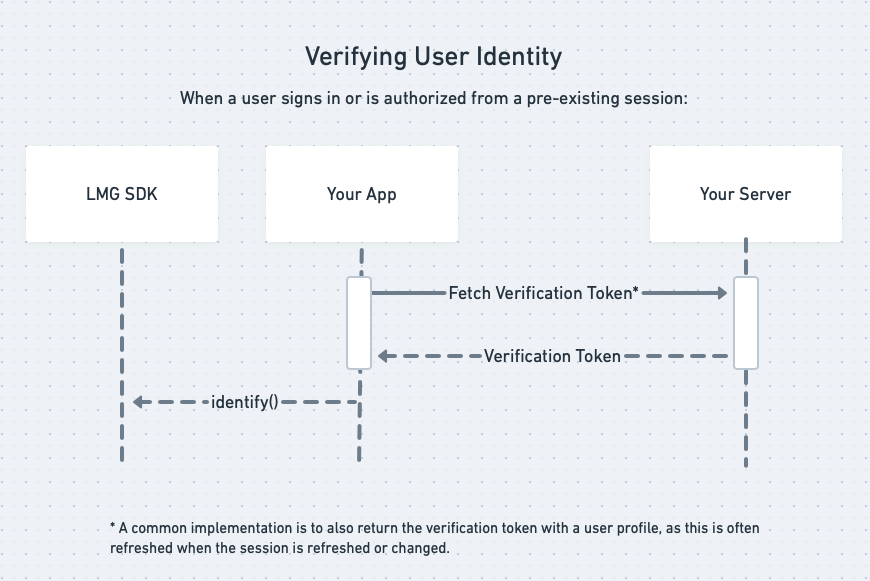
Generating Verification Tokens
To generate a Verification Token you'll need 2 things:
- The Unique User ID that you use to identify this user with the GetintheLoop Platform
- The Verification Key, found in your Property Settings
The Verification Key is a Base64 encoded string that contains an hmacId and an hmacSecret, separated by a semicolon (hmacId;hmacSecret).
Steps
- Decode the Verification Key to get the
hmacIdandhmacSecret - Create a SHA256 HMAC that signs the Unique User ID with the
hmacSecret. The format of this HMAC must be a hex digest string. - Create the final Verification Token by joining the original Verification Key
hmacIdwith your SHA256 HMAC Digest from Step 2, in the formathmacId;timestamp;sha256Digest, and encoding as a Base64 string.
Examples
- Node.js
- PHP
- Java
const assert = require('assert');
const crypto = require('crypto');
const computeSignature = (secret, userId) => {
// 1. Decode the Verification Key
const secretDecoded = Buffer.from(secret, 'base64').toString('utf8');
assert(/^[^;]+;[^;]+$/g.test(secretDecoded));
const [hmacId, hmacSecret] = secretDecoded.split(';')
.map((e) => Buffer.from(e.replace(/-/g, ''), 'hex'));
// 2. Create the SHA256 HMAC digest
const timestamp = Buffer.from(Math.round(new Date() / 1000).toString(16), 'hex');
const hmacDigest = crypto.createHmac('sha256', hmacSecret)
.update(userId).update(timestamp).digest();
// 3. Create the final verification token
return Buffer.concat([hmacId, timestamp, hmacDigest]).toString('base64');
};
const verificationKey = "YOUR_PROPERTY_VERIFICATION_KEY";
const userId = "UNIQUE_USER_ID";
// 3. Encode in final Verification Token format
const verificationToken = computeSignature(verificationKey, userId);
function compute_signature ($secret, $user_id) {
// 1. Decode the Verification Key
$secret_decoded = base64_decode($secret);
list($hmac_id, $hmac_secret) = preg_replace('/-/', '', explode(';', $secret_decoded));
// 2. Create the SHA256 HMAC digest
$timestamp = dechex(time());
$hashdata = $user_id . pack('H*', $timestamp);
$hmac_digest = hash_hmac('sha256', $hashdata, pack('H*', $hmac_secret));
// 3. Create the final verification token
return base64_encode(pack('H*', $hmac_id . $timestamp . $hmac_digest));
}
$verification_key = 'AUDIENCE_VERIFICATION_KEY';
$user_id = 'UNIQUE_USER_ID'; // MUST be the same as provided in identify() call
$verification_token = compute_signature($verification_key, $user_id, $current_date);
import java.util.Base64;
import java.time.Instant;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import javax.crypto.Mac;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.security.InvalidKeyException;
public class Hmac {
private static byte[] hexStringToByteArray(String s)
{
int len = s.length();
byte[] data = new byte[len / 2];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i += 2) {
data[i / 2] = (byte) ((Character.digit(s.charAt(i), 16) << 4)
+ Character.digit(s.charAt(i+1), 16));
}
return data;
}
public static String computeSignature(String secret, String userId) throws NoSuchAlgorithmException, InvalidKeyException
{
// 1. Decode the Verification Key
String[] secretDecoded = new String(Base64.getDecoder().decode(secret), StandardCharsets.UTF_8).split(";");
byte[] hmacId = hexStringToByteArray(secretDecoded[0].replace("-", ""));
byte[] hmacSecret = hexStringToByteArray(secretDecoded[1].replace("-", ""));
// 2. Create the SHA256 HMAC digest
byte[] timestamp = hexStringToByteArray(Long.toHexString(Instant.now().getEpochSecond()));
Mac hasher = Mac.getInstance("HmacSHA256");
hasher.init(new SecretKeySpec(hmacSecret, "HmacSHA256"));
hasher.update(userId.getBytes());
hasher.update(timestamp);
byte[] hmacDigest = hasher.doFinal();
// 3. Create the final verification token
byte[] output = new byte[hmacId.length + timestamp.length + 32];
System.arraycopy(hmacId, 0, output, 0, hmacId.length);
System.arraycopy(timestamp, 0, output, hmacId.length, timestamp.length);
System.arraycopy(hmacDigest, 0, output, hmacId.length + timestamp.length, hmacDigest.length);
return Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(output);
};
}
Security Considerations
In order to be secure the HMAC token must be generated on your server, and communicated to your app or website once the user has been authenticated. Typically implementors return the computed HMAC as part of their user profile payload.